Software Testing Basics: A Comprehensive Guide to Testing Methods and Tools”
Published: 12 Jan 2026
Are you confused about how to start with software testing? You’re not alone, many people find it tricky at first. But don’t worry, in this guide, we’ll walk you through the software testing basics step by step. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of how testing works and why it’s important for building great software. We’ll cover key concepts, methods, and tools you need to know. You’ll also get practical tips to make your testing process smoother. Let’s start in
What is Testing?
Testing is the process of checking something to see if it works as expected. It helps find problems or mistakes before something is used. This can be done with machines, software, or even human skills.
- Testing checks if things work right.
- It helps find and fix problems.
- It’s done before something is used by others.
- Testing helps improve quality.
What is Software Testing?
Software testing is the process of checking if a computer program or app works properly. It helps make sure there are no bugs or errors in the program.
- Software testing makes sure the app works.
- It checks if there are any bugs or mistakes.
- It’s done before the software is given to users.
- Testing helps improve the software’s quality.
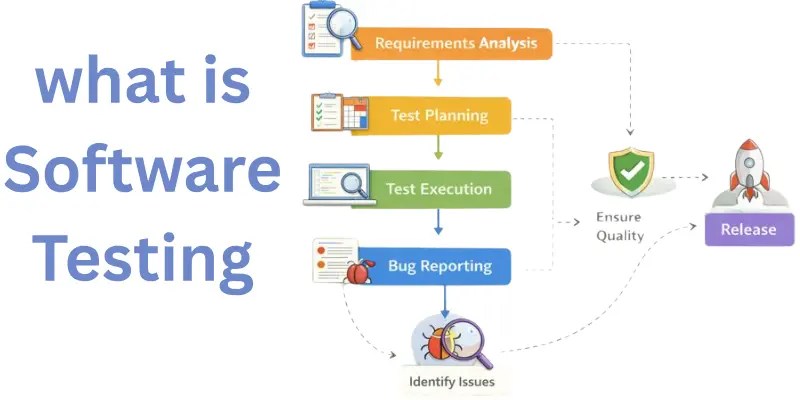
Description of Software Testing
Software testing helps ensure that software is working as it should. It checks different parts of the program to find mistakes. There are many types of software testing, like checking if the software does what it’s supposed to and testing if it works in different situations.
- It checks if the software functions as expected.
- There are different types of tests, like performance or security tests.
- Testing helps make software better and more reliable.
- It helps find problems that users might face later.
Basics of Software Testing
Software testing is the process of checking whether a software program works the way it’s supposed to. The main goal is to find problems early, so the software is reliable, functional, and easy to use. There are a few core concepts in software testing that every tester should know.
The Testing Life Cycle
The testing life cycle is the series of steps that testers follow to make sure the software works as it should. This cycle includes planning, designing test cases, running tests, and fixing any issues. It helps ensure software quality by testing it at different stages of development.
Types of Testing
There are different types of testing that focus on different areas of the software:
- Manual Testing: Testers check the software by hand, running it and looking for bugs.
- Automated Testing: Scripts and tools automatically run tests to check the software faster and more efficiently.
- Functional Testing: Ensures the software does its intended job, like checking if a website’s login works correctly.
Tools for Software Testing
Various tools help testers run tests and track issues. Examples include tools for automated testing like Selenium or JUnit. These tools make the testing process faster and more reliable.
The Basic Steps in Software Testing
- Planning: Testers create a plan based on the software’s requirements. They write test cases to check if each feature works.
- Execution: Tests are run, and results are recorded to see if the software passes or fails.
- Logging Defects: If issues or defects are found, they are recorded in a report to be fixed.
- Delivery of Results: Once testing is done, the test results are shared with the development team for improvements.

Software Test Engineer’s Role in Testing
What Does a Software Test Engineer Do?
A software test engineer plays a key role in software testing by ensuring the software works as expected.
- Designing Tests: Creating test plans and test cases based on software requirements.
- Running Tests: Testing the software manually or using automated tools.
- Reporting Bugs: Identifying issues and reporting them to the development team for fixing.
A software test engineer is responsible for designing and executing tests to ensure that the software meets its intended requirements. This helps find problems early and ensures the software is reliable.
What is a Software Test?
Software testing is a set of activities performed to check if the software works as intended. Key points of software testing include:
- Activities: Performing tasks to identify defects or bugs in the software.
- Conditions: Testing under different conditions to ensure the software works in various scenarios.
- Types: Includes manual testing and automated testing to check the software’s functionality.
A software test is a set of activities performed to identify defects in software and ensure its correctness, reliability, and performance. Proper software testing helps improve the quality and performance of the software.
Importance of a Software Test Engineer
A software test engineer is crucial to the software testing process. Their importance includes:
- Preventing Bugs: Catching issues before the software is released to users.
- Ensuring Quality: Making sure the software meets the intended functionality and performance standards.
- Improving User Experience: Helping deliver a bug-free, smooth experience for users.
Software test engineers ensure that all aspects of the software are thoroughly tested for quality before release. Their work in software testing ensures the software is reliable, leading to fewer problems for users and better overall satisfaction

What Do You Know About Software Testing?
Understanding the Fundamentals of Testing
Software testing is a critical part of software development. It’s about making sure the software works as it should before it’s used by real people. The goal is to find and fix any problems (bugs) before the software is released. Testing ensures that software is reliable, functional, and user-friendly.
Understanding the basics of testing, including its goals, methodologies, and tools, is crucial for every software professional. By understanding these fundamentals, testers can help improve the quality of software and reduce the risk of defects in the final product.
Goals of Software Testing
- Ensuring Functionality: Make sure the software does what it’s supposed to do.
- Finding Bugs: Identify and fix any issues or defects in the software.
- Ensuring Performance: Test if the software works well under different conditions, like high traffic on a website.
- Improving User Experience: Ensure the software is easy to use and doesn’t confuse users.
Methodologies in Software Testing
There are various methodologies used in software testing to ensure thorough checks. Some common ones include:
- Manual Testing: Testers check the software by interacting with it directly, just like a real user.
- Automated Testing: Tests are run using tools or scripts, saving time and ensuring faster checks.
- Unit Testing: Testing small parts of the software individually to ensure they work properly.
- Integration Testing: Testing how different parts of the software work together.
In real-life scenarios, testers may manually check if a website’s “Add to Cart” button works correctly, while automated tools like Selenium might be used to test how well the site handles many users at once.
Tools for Software Testing
There are several tools available for software testing, each serving a different purpose. Some popular ones include:
- Selenium: A tool used for automated testing of web applications. It helps testers run tests across different browsers quickly and efficiently.
- Jira: A tool used for tracking defects and managing testing activities.
- JUnit: A framework used for running tests in Java-based applications.
What Every Software Tester Should Know
Every software tester must have a strong understanding of key concepts in software testing. This knowledge includes:
- Testing Principles: Understanding why and how testing is done to find issues early and ensure quality.
- Testing Techniques: Knowing how to test different parts of software. For example, using unit testing to check individual functions or performance testing to see how well the software handles a lot of users.
- Tools: Knowing how to use tools like Selenium for automated testing, which speeds up the process and ensures more accurate results.
Knowledge of testing principles, different testing techniques, and tools like Selenium is key for software testers. This expertise helps testers perform their jobs more effectively, leading to better software quality and a smoother user experience.
Types of Software Testing
Software testing comes in different types. Each type checks different things in the software. Here are some of the main types of testing:
Manual Testing
- What it is: A tester checks the software by using it like a real user would.
- When it’s used: Used when automated testing is not possible or when testing early in the process.
- Example: Clicking through a website to make sure buttons and links work.
Automated Testing
- What it is: Special tools or scripts run tests automatically without human help.
- When it’s used: Used when you need to test the software quickly or many times.
- Example: Using a tool like Selenium to check if a web page works on different browsers.
Unit Testing
- What it is: Testing small parts of the software, like a single function or feature.
- When it’s used: Done early to check if each part works well.
- Example: Testing a calculator app to make sure it adds numbers correctly.
Integration Testing
- What it is: Checking if different parts of the software work together.
- When it’s used: After unit testing, to make sure all parts of the software communicate properly.
- Example: Testing if the login system works with the database and payment system.
Functional Testing
- What it is: Making sure the software does what it’s supposed to do.
- When it’s used: Used to check if the software works as expected.
- Example: Testing if an online store correctly adds items to the shopping cart.
Performance Testing
- What it is: Testing how well the software works under heavy use or load.
- When it’s used: To check if the software can handle many users at once.
- Example: Testing if a website works well with 1000 visitors at the same time.
Security Testing
- What it is: Checking if the software is safe from threats and attacks.
- When it’s used: Used for software that handles sensitive data, like banking apps.
- Example: Testing if a website’s payment page is secure from hackers.
Usability Testing
- What it is: Testing if the software is easy to use and understand.
- When it’s used: Done to make sure the software is user-friendly.
- Example: Asking real users to try an app and give feedback on how easy it is to use.
Regression Testing
- What it is: Testing to see if new changes have caused any problems with the software.
- When it’s used: After updates or bug fixes.
- Example: After adding a new feature to an app, making sure that old features still work, like sending messages.
Acceptance Testing
- What it is: Making sure the software meets the customer’s needs and is ready for use.
- When it’s used: Done before the software is released to the public.
- Example: Testing an online store to make sure everything works as planned, like correct
The Importance of Software Testing in Software Development

Why is Software Testing Important?
Software testing is critical for identifying and fixing bugs, ensuring functionality, and improving overall software quality.
- Identifying Bugs Early: Testing catches bugs early, making them easier and cheaper to fix. For example, testing a login feature can catch issues before they become bigger problems.
- Ensuring Functionality: Testing makes sure the software works as expected. For instance, testing the checkout process on an online store ensures customers can complete their purchases.
- Improving Quality: Testing improves software reliability. For example, catching bugs in a payment system prevents bad user experiences.
Simple Example
A tester finds a website crashes with many users; fixing this ensures the site doesn’t fail during high traffic.
Testing prevents bugs, like missing user data, from affecting users after launch.
Software Testing Basics for Development Teams
Integrating Testing into the Development Life Cycle
The basics of software testing should be part of every development process to prevent defects from reaching the end user.
Why Start Testing Early?
- Catch Defects Early: Testing early makes it cheaper and easier to fix bugs.
- Prevent Major Problems: Early testing reduces the risk of big issues later.
The Role of Testers
Testers ensure the software works correctly and efficiently, reducing the chance of issues later.
Simple Steps for Testing:
- Planning: Decide what needs testing and create test cases.
- Test Early: Start testing as soon as possible.
- Execute Tests: Run tests and report bugs.
- Repeat: Keep testing as new features are added.
Key Concepts in Software Testing
- Test Cases: A test case defines the conditions for testing the software, including the input, expected output, and steps. Example: A test case for login might check if the user can log in with a valid username and password.
- Test Plans: A test plan outlines the testing process, including the scope, objectives, and schedule. Example: A test plan might include tests for login, adding items to the cart, and completing checkout.
- Defect Tracking: Tracking issues found during testing to ensure they’re resolved before release. Example: A bug in the payment system is logged and tracked until it’s fixed.
Software testing basics involve understanding test cases, defect tracking, and the testing life cycle.
Conclusion
Today, we’ve covered a lot about software testing from key concepts like test cases, test plans, and defect tracking, to the different testing approaches like manual, automated, and unit testing. These basics are essential for anyone involved in software development, as they help ensure that software is functional, reliable, and ready for release. My personal recommendation is to start integrating software testing early in your development process. It’s a game-changer for catching bugs before they become major problems, saving time and improving the quality of your product. So, folks, keep testing, keep learning, and stay tuned for more tips and insights on building better software!.
The main goal of software testing is to ensure that the software works as expected. It helps find bugs or errors that can affect performance. Testing makes sure the software is reliable, secure, and meets the user’s needs. Without it, users might experience problems after launch.
Software testing improves quality by identifying issues before they reach the user. It helps developers fix bugs early, which leads to fewer problems later. Testing ensures the software meets performance standards and works smoothly. It also makes the software user-friendly.
In manual testing, a person checks the software by performing actions like a real user. Automated testing uses scripts or tools to run tests automatically. Manual testing is great for new features or small tests, while automated testing works well for repetitive tasks and larger projects.
Starting testing early helps catch bugs before they get too complicated. It saves time and money in the long run by fixing small issues early. Testing early also ensures that developers stay on track with the software’s intended goals. Early testing results in better software quality overall
A defect is an issue or bug found during software testing. It means the software doesn’t behave as expected or has an error that needs fixing. Defects can affect functionality, security, or user experience. Identifying defects early ensures they are fixed before users encounter them.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks